Introduction
Material requirement planning is a system that is used to manage the manufacturing process through effective planning and an inventory control system. This Material Requirement Planning is basically a planning tool that manages the production operations.

How MRP (Material Requirement Planning) Works
MRP (Material Requirement Planning) works by arranging the material from the supplier. Material required for the production is automatically arranged by the supplier. Sometimes different software, like SAP, Oracle, and IBM, is used to arrange the materials. Software generates the planning from the demand forecast, and the planning generates the material requirement, i.e., how much material is required and when the material is required. This material calculation is based on BOMs. (Bill of Materials).
Material Requirement Planning can be done manually, or by utilizing MS Excel or the most advanced systems like SAP HANA.
Objective of Material Requirement Planning
The objective of MRP (Material Requirement Planning) is to ensure that the raw material is available on time to execute the planned production. Do not pile up the level of inventories, and the inventories must be under control. There must be proper scheduling for the purchase of materials and the dispatch of raw materials. Sufficient inventory levels to cater to the market needs.
The main objective of MRP (Material Requirement Planning) is to reduce the excessive work in process levels, raw materials, and finished goods inventories. Pile up of stock is an extra burden to the financial cost, so the company usually avoids it.
Requirements to run Material Requirement Planning
The following are the requirements to run Material requirement planning
- BOMs (Bill of Materials)
- Inventory data of raw materials and finished goods.
- Master production schedule
The objective of Material requirement planning is to ensure the material availability required for production.
There is certain information required for Material requirement planning
- Monthly Forecast for all products and SKUs.
- Lead time to arrange the materials
- Lead time for the production of each product
- Batch sizes
- BOM of all the raw materials required to produce
- Opening inventory stock levels of all raw materials
- Safety stock requirement
- An order that has not been fulfilled for raw materials
Production Scheduling
Production scheduling, when it is validated and uploaded to the software, is called master production scheduling. Master production scheduling will cover the following aspects, and it is an important part of Material Requirement Planning. MPS is based on demand forecast, customer orders, and available production capacities.
Production Scheduling Success: Expectations to Aim For and Pitfalls to Avoid
“Learn how to master production scheduling in pharmaceuticals: set expectations, avoid common pitfalls, plan forecasts, capacities & performance.
- What products will produce?
- When are products required?
- How much is required?
- Capacity of manufacturing?
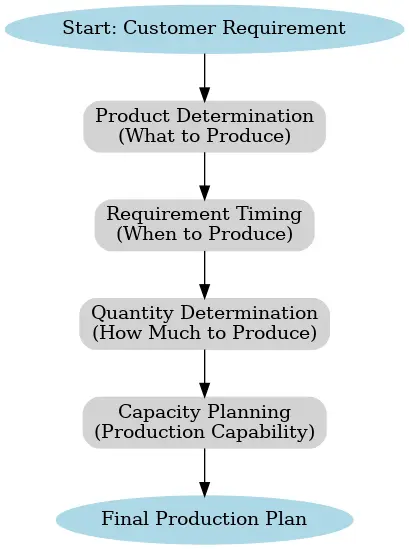
First Portion: Product Determination
This section focuses on identifying what product will be produced. The requirements are derived from customer demands. Based on these requirements, the planner decides which products need to be manufactured and creates a corresponding production plan.
The planning process can be carried out using different tools and methods, such as:
- SAP HANA
- MS Excel
- Oracle
- IBM
Second Portion: Product Requirement Timing
This section explains when products are required. Each organization maintains a safety stock to ensure smooth operations. The inventory level determines when a product needs to be replenished.
- If the inventory level reaches the predefined limit, the system automatically generates a requirement for replenishment before further decline occurs.
- Once this requirement is generated, the planner will schedule and plan the production of the needed product accordingly.
Third Portion: Quantity Required
This section outlines the quantity of each product required. The forecast for each product includes the required quantities monthly.
- These forecasts help the planner determine the production quantities for each month.
- Proper planning ensures that inventory levels are maintained efficiently and stock shortages are avoided.
Fourth Portion: Production Capacity
Manufacturing depends on the available production capacities. Each machine has defined limitations on how many packs it can produce. Machines cannot operate beyond their specified capacities.
A well-prepared plan should:
- In cases where the forecasted demand exceeds current capacity, include strategies for capacity enhancement (e.g., adding shifts, upgrading equipment, or investing in new machinery).
- Align product quantities with the existing production capacities.
MPS should not exceed the production capacities.
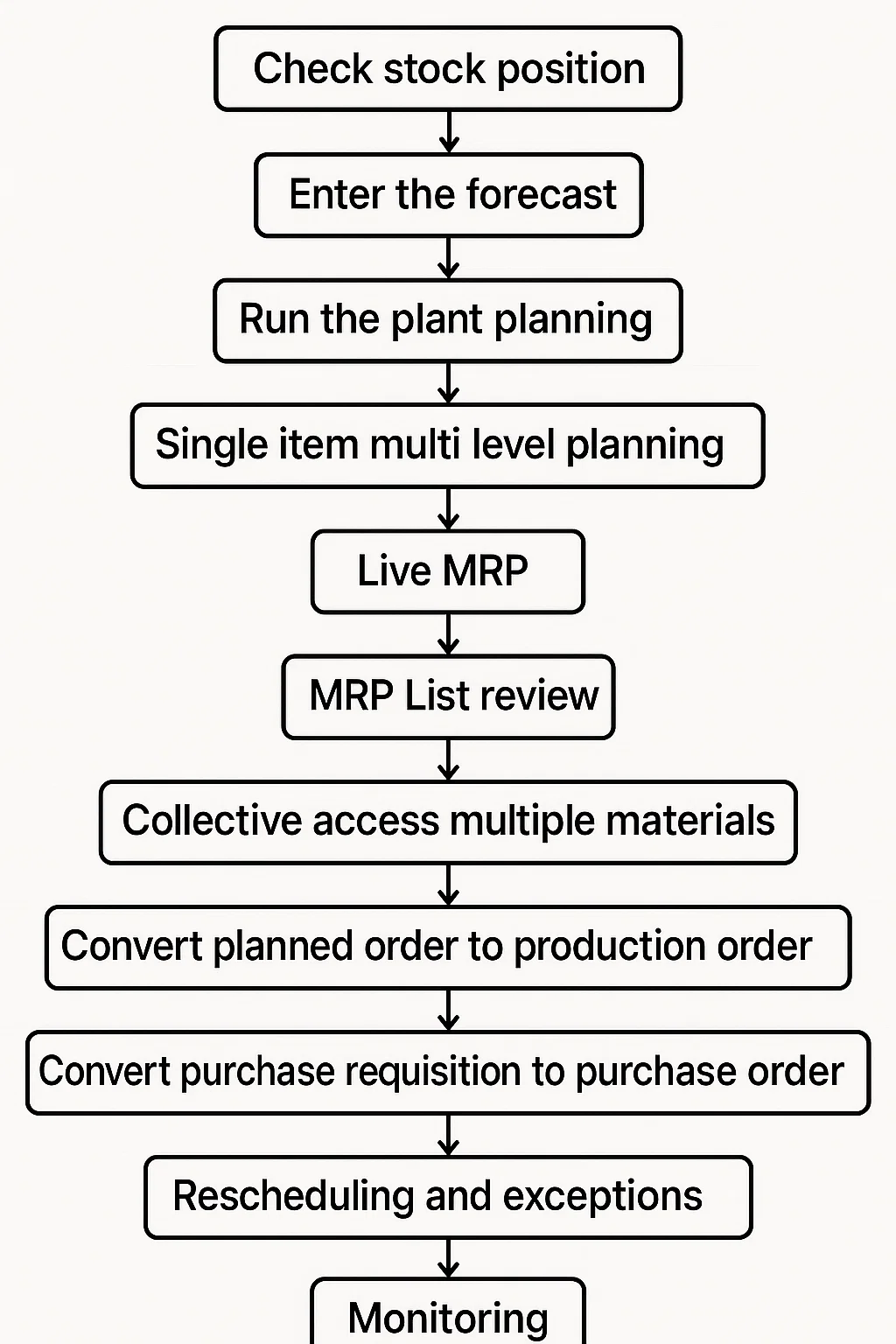
Steps of Material Requirement Planning
These are the following steps of Material Requirement Planning
1-Data Collection
First, we need to collect the data, production schedule, BOM, and inventory records.
- Production schedule: Review the MPS to determine what and when needs to be produced.
- BOM: It is the list of ingredients required to produce a product. Bill of materials contains ingredients/ component names and the quantity.
- Inventory records: What are the current stock levels of finished goods and raw materials? Finished goods stocks will decide how much quantity needs to be produced, and raw material stock quantity will decide how much to order as per the available lead time from the vendors for the materials’ availability.
2-Net Requirement
Requirement generated from the MPS and BOM. Check the inventory levels
- to see if raw materials are in stock, so no need to order.
- If the raw material stock is out of the safety stock level, then an order needs to be generated to keep the minimum inventory level in hand.
Consider an example below,
- Product Name: ABC
- Current Month: January:
- Forecast: 5000 packs
- FG Inventory: 10,000 packs
- Inventory Policy: 3 Months Raw Material Stock and FG stock
Current Scenario for the finished goods Stock:
Finished Goods (FG) Stock Management Case
- Current FG stock levels have declined to 5,000 packs, which is below the policy requirement.
- The forecasted demand is 5,000 packs per month.
- The stock maintenance policy level is 15,000 packs.
Plan:
- One batch per month is planned.
- This ensures that:
- Monthly Input = Monthly Output (5,000 packs).
- No inventory pile-up occurs.
- No shortages arise.
- Over 3 months, the stock will remain balanced at the required forecast level, maintaining a continuous supply while aligning with policy.
BOM: Product Name: ABC, Batch Size: 5000 packs
- Material A ——-10 K
- Material B _____ 5 Kg
- Material C _______ 2 kg
MPS: 5000 packs per month
Raw Material Stock Status:
- Material A: 20 Kg
- Material B: 10 Kg
- Material C: 2 Kg
Current Scenario for the Raw Material Stock:
As per the above data of RM stock, material is not available as per the 3-month inventory policy. A software-based Material Requirement Planning system will automatically maintain the materials level. Reordering will be generated when material stocks reach lower than the mentioned quantity.
| Component | Available | Required | Stock to be arranged |
| Material A | 20 Kg | 10 Kg | 20 Kg |
| Material B | 10 Kg | 5 Kg | 10 Kg |
| Material C | 2 Kg | 2 Kg | 6 Kg |
Stock will be arranged as per the above-mentioned stock levels.
- Material A: 20 Kg on order because of three months stock policy. 10 kg left after Issuance of 10 kg from the stock, so replenishment of 20 kg is required to maintain the stock levels.
- Material B: 10 kg on order because of three months stock policy. 5 kg stock is left after issuance of 5 kg from the stock, so replenishment of 10 kg is required to maintain the stock levels.
- Material C: 6 kg on order because of three months stock policy. Stock is empty after the issuance of 2 kg for the batch, so 6 kg material is required in inventory for the purchase.
3-Material Ordering Size
- Each material has a specified batch size that defines how much can be produced in one run.
- Raw materials are produced or procured according to these batch size specifications.
- Many organizations operate under Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) policies:
- They may also be required to purchase raw materials in MOQ lots from suppliers.
- They will not sell less than the defined MOQ.
- In production planning, the organization must decide between:
- Fixed Order Quantity (FOQ): Ordering or producing a fixed amount each time.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): A calculated order size that minimizes total costs (ordering + holding costs).
4-Time Phasing
Each material ordering must be time-bound. Material must reach on time to maintain the inventory levels. There should not be any delay in ordering. Ordering may be done via the use of software or can be done manually.
5-System Alertness
Material Requirement Planning utilizes the software that enables to initiation of an alarm to reorder the quantity, reschedule the order, or, in any unavoidable circumstances, cancel the order. This system alert also checks the MPS and FG stock levels. If there is any change in product demand, it will provide an alert. This can happen in case of high sales or low sales.
Challenges in Material Requirement Planning
- Incorrect data may mislead the procurement of materials, inventory management. Data integrity is most important in Material Requirement Planning
- An incorrect BOM may produce misleading information. It is very much necessary to have correct BOM data. Any outlier may impact the whole production planning. All components must be present in the BOM. Any missing component will produce false planning.
- MRP is dependent on demand forecast; if the forecast is wrong, it might impact on market, resulting in a shortage of stock or excess inventories.
- Supplier delays may lead to an impact on MRP as the material is not arranged timely manner due to any reason so which will impact on production planning and market stock.
- Weather conditions or any other unwanted situation may impact the Material Requirement Planning
- Machine breakouts and quality issues in the product may produce a shortage in inventory levels.
- Advancements in software for ERP require a huge investment along with people development in the software usage.