Operational excellence (OpEx) is more than a collection of tools and methodologies; it is a philosophy aimed at achieving sustainable growth, innovation, and efficiency. At its core, operational excellence involves a commitment to consistently delivering value to customers, stakeholders, and employees. It encompasses optimizing processes, empowering teams, and creating a culture where continuous improvement is not just encouraged but ingrained in the organizational DNA. While methodologies like Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen provide frameworks and tools to drive process efficiency, these approaches alone cannot guarantee sustained success. True operational excellence transcends the application of these tools. It requires a holistic mindset that integrates technical efficiency with human-centered leadership. At the heart of this philosophy lies leadership, the driving force that inspires teams, shapes culture, and ensures alignment with strategic objectives.
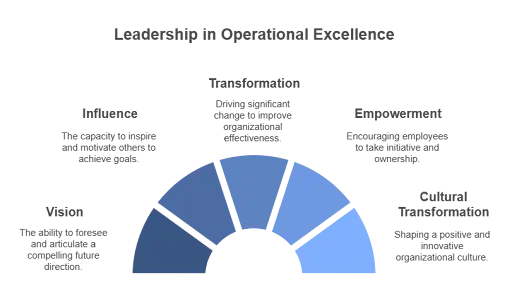
Leadership in operational excellence is not merely about authority or management; it is about vision, influence, and transformation. Effective leaders serve as catalysts for change, navigating their organizations through complex challenges while fostering a shared sense of purpose. They create an environment where employees feel empowered to innovate, collaborate, and take ownership of their contributions to the organization’s goals.
This article delves into the multifaceted role of leadership in operational excellence, focusing on the attributes of effective leaders, their impact on teams, and their ability to drive cultural transformation. It examines how leadership extends beyond the operational aspects of efficiency to address the deeper elements of trust, engagement, and shared accountability. By doing so, leaders not only achieve short-term improvements but also build resilient organizations capable of thriving in dynamic and competitive markets
The Role of Leadership in Operational Excellence
Leadership serves as the cornerstone of operational excellence. It is the force that bridges the gap between strategy and execution, ensuring that organizational goals are translated into actionable initiatives. Leaders play several pivotal roles in this process:
1. Vision Setting and Strategic Direction:
A leader’s primary role in operational excellence is to articulate a clear and compelling vision. This vision serves as a north star, guiding teams and departments toward a common objective. An effective leader ensures that this vision aligns with the principles of operational excellence, emphasizing efficiency, innovation, and value creation.
The ability to set a strategic direction involves not only defining where the organization needs to go but also identifying how it will get there. Leaders must:
- Communicate Vision Clearly: Employees need to understand how their individual roles contribute to the organization’s broader goals. Clear communication fosters alignment and ensures that everyone is moving in the same direction.
- Inspire Commitment: A compelling vision motivates employees to give their best efforts. Leaders inspire commitment by connecting the vision to a sense of purpose and by demonstrating their dedication to operational excellence.
- Adapt Strategies as Needed: Markets and industries are constantly evolving. Effective leaders remain flexible, adjusting their strategies to meet changing circumstances while staying true to the core principles of operational excellence.
2. Culture Building and Transformation:
Operational excellence is as much about culture as it is about processes. Leaders play a critical role in shaping the organizational culture, fostering an environment that supports continuous improvement and innovation. They achieve this by:
- Modeling Desired Behaviors: Leaders set the tone for the organization. By embodying the principles of operational excellence, they encourage their teams to do the same.
- Encouraging Open Communication: A culture of openness and transparency is essential for identifying areas of improvement. Leaders create safe spaces for employees to voice concerns, share ideas, and offer feedback without fear of retribution.
- Reinforcing Core Values: Core values act as guiding principles for decision-making and behavior. Leaders ensure that these values are consistently upheld across all levels of the organization.
- Communicating the “Why”: People are more likely to embrace change when they understand its purpose. Leaders articulate the “why” behind operational excellence initiatives, linking them to organizational success and individual growth.
- Encouraging Feedback and Adaptation: Culture change is an iterative process. Leaders encourage feedback, using it to refine strategies and address gaps. Open dialogue fosters trust and ensures alignment with cultural objectives.
3. Employee Engagement and Empowerment:
Engaged employees are the driving force behind operational excellence. Leaders foster engagement by creating a work environment where employees feel valued, motivated, and empowered to contribute to the organization’s success.
Empowerment involves:
- Providing Autonomy: Leaders trust their teams to make decisions within their areas of expertise, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Investing in Development: Training and development opportunities equip employees with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in their roles. Leaders prioritize continuous learning as a cornerstone of operational excellence.
- Recognizing Achievements: Celebrating successes small or big boosts morale and reinforces the behaviors and practices that contribute to operational excellence.
4. Driving Continuous Improvement:
Leaders champion the philosophy of continuous improvement, encouraging teams to seek out and implement incremental changes that enhance efficiency and quality. This requires a proactive approach to identifying inefficiencies and addressing them before they escalate into larger issues.
Key strategies include:
- Promoting Kaizen Events: Kaizen, or “change for the better,” involves collaborative problem-solving sessions that engage employees at all levels. Leaders facilitate these events to uncover improvement opportunities and implement effective solutions.
- Leveraging Data and Analytics: Informed decision-making is a hallmark of operational excellence. Leaders use data-driven insights to monitor performance, identify trends, and guide improvement efforts.
- Encouraging Innovation: Operational excellence is not just about doing things better—it’s also about doing things differently. Leaders foster a culture of innovation, encouraging teams to think creatively and challenge the status quo.
5. Ensuring Accountability and Alignment:
Operational excellence requires alignment between individual, departmental, and organizational goals. Leaders play a crucial role in establishing accountability systems that ensure everyone is working toward the same objectives.
This involves:
- Setting Clear Expectations: Employees need to know what is expected of them and how their performance will be measured. Leaders provide clarity by defining roles, responsibilities, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Monitoring Progress: Regular reviews and performance evaluations help leaders track progress and identify areas for improvement. This feedback loop is essential for maintaining momentum and focus.
- Addressing Challenges Head-On: When obstacles arise, leaders take a proactive approach to resolving them, ensuring that teams remain aligned and on track.
The Attributes of a Good Leader
Good leaders exhibit traits that inspire trust, engagement, and motivation. Key attributes include:
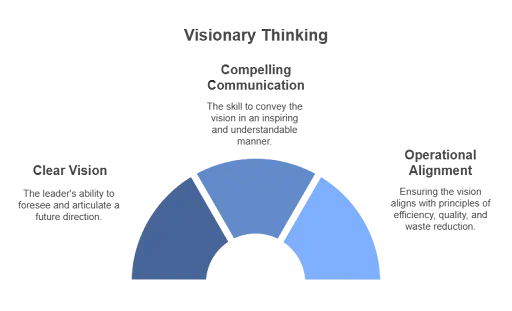
Visionary Thinking:
An effective leader has a clear vision for the organization’s future and communicates it compellingly. They ensure the vision aligns with operational excellence principles, such as reducing waste, enhancing quality, and improving efficiency.
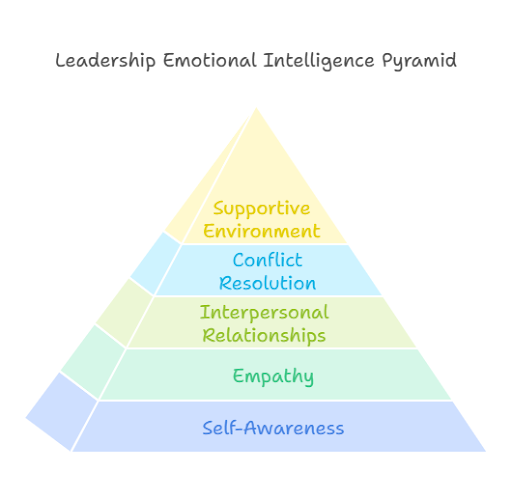
Emotional Intelligence (EI):
Emotional intelligence is the ability to understand and manage one’s emotions while empathizing with others. Leaders with high EI:
- Build strong interpersonal relationships.
- Resolve conflicts effectively.
- Create an inclusive and supportive environment.
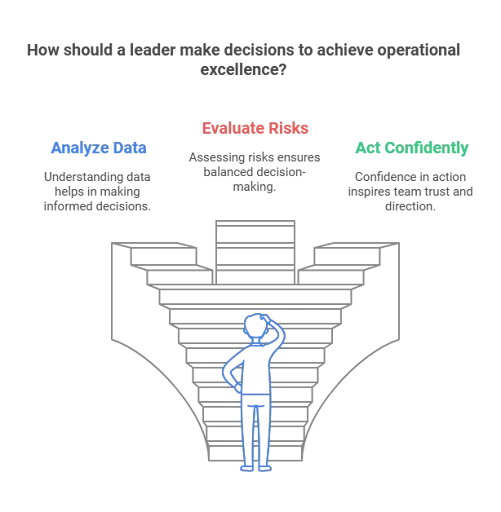
Decisiveness:
Operational excellence requires prompt and informed decision-making. Leaders must analyze data, evaluate risks, and act confidently to steer their teams.
Resilience and Adaptability:
The journey to operational excellence is fraught with challenges. A resilient leader remains composed under pressure, while adaptability ensures they respond effectively to dynamic market conditions.
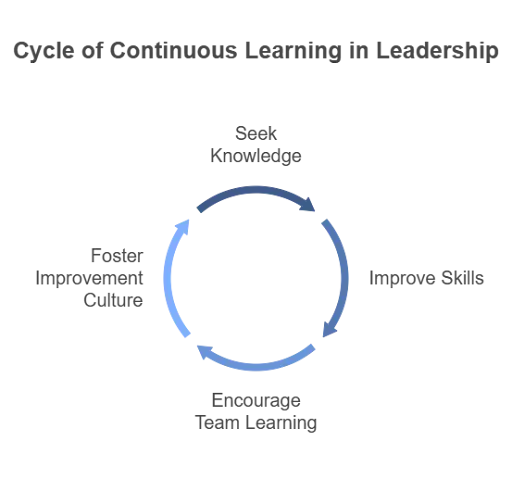
Commitment to Learning:
Leaders in OpEx are lifelong learners, constantly seeking to improve their knowledge and skills. They encourage the same mindset in their teams, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Leadership Strategies for Operational Excellence
1. Setting Clear Goals and Metrics:
Effective leaders establish a roadmap for success by defining SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals. Clear objectives provide focus, while metrics such as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure performance and highlight areas for improvement. Leaders must:
- Regularly communicate these goals to the team.
- Use real-time dashboards and analytics to ensure transparency and track progress.
- Encourage alignment of individual and team objectives with the organization’s broader mission.
2. Fostering Continuous Improvement: Leaders act as catalysts for a culture of continuous improvement, which is integral to OpEx. Key actions include:
- Promoting Kaizen Events: These structured workshops bring teams together to identify inefficiencies, brainstorm solutions, and implement quick wins.
- Empowering Employees: Encouraging staff to suggest improvements ensures their involvement and commitment to process optimization.
- Celebrating Small Wins: Recognizing incremental successes reinforces progress and motivates teams to persist in their improvement efforts.
3. Developing Talent: Leadership commitment to employee growth builds a resilient and skilled workforce. Strategies include:
- Training Programs: Investing in training for Lean, Six Sigma, and other OpEx methodologies equips employees with tools for enhancing efficiency.
- Mentoring: Leaders guide emerging talent to develop problem-solving and decision-making skills, ensuring a pipeline of future leaders.
- Career Development Opportunities: Structured growth pathways foster loyalty and improve retention.
4. Leveraging Technology: Digital tools and automation are critical enablers of operational excellence. Leaders must:
- Champion Adoption: Emphasize integrating technology such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced analytics.
- Promote Digital Fluency: Train teams to utilize these tools effectively.
- Continuously Evaluate Tools: Ensure that adopted technologies remain aligned with organizational goals.
5. Aligning Processes with Strategy: Operational processes should consistently support the organization’s strategic objectives. Leaders ensure alignment through:
- Value Stream Mapping: Visualizing end-to-end processes to identify bottlenecks and streamline workflows.
- Eliminating Waste: Adopting Lean principles to remove non-value-added activities.
- Standardizing Best Practices: Developing and implementing repeatable, efficient methods across the organization.
Measuring Leadership Effectiveness in Operational Excellence
Measuring leadership effectiveness in driving operational excellence involves evaluating how well leaders enable their teams and organizations to achieve sustainable, efficient, and innovative outcomes. Below are key metrics and approaches for assessing leadership effectiveness in this context:
1. Achievement of Operational Goals:
- KPI Performance: Evaluate the attainment of key performance indicators (KPIs) related to operational excellence, such as:
- Cycle time reduction.
- First-pass yield improvement.
- Cost savings through process optimization.
- Customer satisfaction scores.
- Alignment with Strategic Objectives: Assess whether operational improvements align with broader organizational goals.
2. Employee Engagement and Empowerment:
- Employee Feedback: Conduct surveys or interviews to gauge employee satisfaction, trust in leadership, and perceptions of empowerment.
- Participation Rates: Monitor employee involvement in continuous improvement initiatives, such as Kaizen events or Lean projects.
- Turnover Rates: High retention often indicates effective leadership in creating a supportive and motivating environment.
3. Implementation of Continuous Improvement Initiatives:
- Frequency of Improvement Projects: Track how often leaders initiate or support projects aimed at reducing inefficiencies or enhancing processes.
- Sustainability of Changes: Measure the longevity and effectiveness of implemented improvements.
4. Development of Talent:
- Training Metrics: Analyze the number of employees trained in operational excellence methodologies (e.g., Lean, Six Sigma).
- Promotion Rates: Track the advancement of team members to leadership roles, reflecting mentoring success.
- Skill Assessment: Measure improvements in employee competencies through regular evaluations.
5. Use of Data-Driven Decision-Making:
- Quality of Decisions: Evaluate how effectively leaders use data and analytics to make operational decisions.
- Responsiveness to Trends: Assess how quickly leaders identify and address emerging inefficiencies or opportunities.
6. Organizational Culture and Alignment:
- Cultural Audits: Conduct audits to determine the extent to which operational excellence principles are embedded in the organization’s culture.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Measure the effectiveness of communication and cooperation across teams, driven by leadership.
7. Innovation and Adaptability:
- Adoption of New Technologies: Monitor how actively leaders champion the implementation of new tools and technologies for operational excellence.
- Adaptation to Change: Assess the leader’s ability to steer teams through disruptions or shifts in strategy while maintaining performance.
8. External Recognition:
- Benchmarking: Compare the organization’s operational metrics with industry standards.
- Awards or Certifications: Achievements such as Lean Six Sigma certifications or industry awards can reflect leadership effectiveness.
9. Financial Impact:
- Cost Reductions: Evaluate savings resulting from process improvements.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measure ROI for initiatives spearheaded by leadership in operational excellence.
- Profitability Growth: Assess whether operational excellence efforts contribute to the organization’s financial performance.
10. Crisis Management and Resilience:
- Incident Response: Review how effectively leaders manage operational disruptions.
- Resilience Metrics: Assess the organization’s ability to recover quickly from setbacks under their leadership.
By combining quantitative metrics (e.g., KPI achievements) with qualitative insights (e.g., employee feedback), organizations can holistically measure leadership effectiveness in operational excellence. Regular assessments and adjustments based on these findings ensure sustained progress and adaptability.
Leadership is the cornerstone of operational excellence. Effective leaders inspire teams, foster collaboration, and drive cultural transformation. By embodying the principles of OpEx, they ensure sustainable success in an ever-changing business environment. To be a leader in operational excellence is to commit to a journey of continuous improvement, innovation, and empowerment. It requires not only technical proficiency but also the ability to connect with and inspire others. In doing so, leaders become catalysts for change, unlocking the full potential of their organizations and teams.