This article clarifies the importance of cGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practices) in drug manufacturing and the role of GMP in ensuring product quality. The product manufacturing process must be reproducible and consistent. The system of audit and compliance is designed to ensure that GMP is properly in place and being used.
Definition of GMP
GMP is defined as good manufacturing practices that ensure the safety, identity, strength, purity, and quality of the product.
WHO defines GMP: “GMP Good Manufacturing Practices is a system for ensuring that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.”
Good manufacturing practices begin with the personnel entering the facility. Every person is responsible for working as per the defined procedures of GMP.
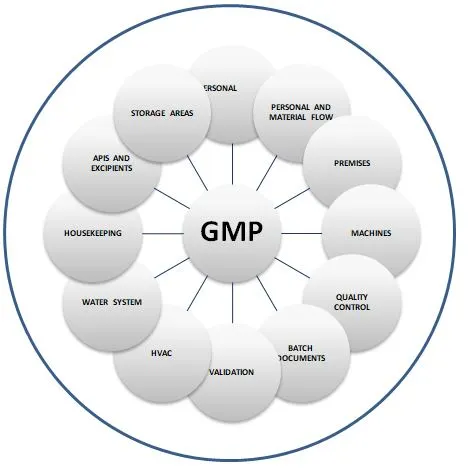
Factors Impacting GMP
The following are the factors that may impact GMP either directly or indirectly.
- Personal
- Personal and Material Flow
- Premises
- Machines
- Quality Control
- Batch Documents
- Validation
- HVAC system
- Water system
- Housekeeping system
- Approved APIs and Excipients
- Storage Areas
Personnel
Personnel have high importance in GMP implementation. Why are personnel important in good manufacturing?
Because humans contain trillions of microorganisms, these microorganisms can directly increase the microbial burden in manufacturing areas. If a person does not wear proper gowning and maintain good hygiene, will you imagine? What would happen? There is a chance of contamination in the drug product, which could be harmful to patients. Personals are a major source of contamination, and they must follow the standard operating procedures.
Personal behavior is vital in maintaining GMP. A written procedure is in place for personnel entering the premises. Eating, drinking, and personal medications are not allowed in production premises and storage areas. There must be a proper dedicated facility for such purposes. Jewellery and personal gadgets are also prohibited in production areas.
Personnel Medical Examination
Personnel working in the factory must be fit medically. Personnel, not having any contagious diseases, bruising, or skin disease. It is mandatory to conduct a medical examination of each individual before joining and to undergo periodic medical examinations as per the company’s decided policy to ensure a safe work environment and prevent contamination.
Sanitation and Personnel Hygiene
Sanitation and Hygiene are important aspects of GMP, and personnel should wear clean clothes. They should not have open wounds. Personnel should maintain a high standard of cleanliness to prevent the chances of contamination.
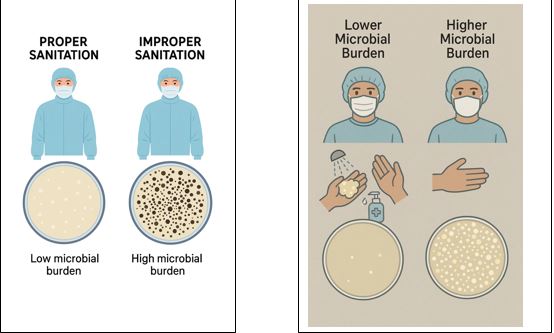
Consider an example of good Hygiene:
Two Humans were considered as a sample to check the microbial burden.
The first person has properly taken a shower, washed their hands, sanitized with hand sanitizer, and worn proper gowning.
The second person did not take a shower, did not wash their hands, and did not sanitize their hands with hand sanitizer, but wore proper gowning.
Swab samples were collected from the hands and gowns of both persons. The results are clear and loud in the display mentioned below.
Personnel Behaviors
Attitude and behavior in pharmaceutical operations are of extreme importance. Humans are more prone to violate rules due to their social dependencies, i.e., hugging, shaking hands, and gossiping during operations. Personnel must receive proper training in GMP practices and refrain from engaging in poor practices. Rules and pictorials must be placed in the native language to provide better understanding.

Handling Of Visitors
Personnel who are not working in the factory are considered visitors. Handling of visitors must be mentioned in the SOP. A visitor may be a vendor, auditor, fabricator, etc. Visitors must be medically fit and free from any skin diseases, open wounds, or contagious illnesses. There should be proper gowning protocol for visitors as well, and the use of PPEs as recommended for pharmaceutical personnel to ensure GMP.
Qualified Personnel:
Qualified personnel have expertise in the desired operation, and GMP demands qualified personnel to ensure the safety, identity, strength, purity, and quality of the product. This is another aspect of GMP. Qualified personnel are trained for dedicated operations. Qualified personnel can operate and troubleshoot. All critical steps must be done by qualified personnel. There must be dedicated, qualified personnel in Production and QC for in-process control monitoring, equipment, and instrument operations.
Gowning and De-Gowning
Gowning and De-Gowning are important aspects of GMP. There should be a written procedure for gowning and de-gowning. It is mandatory for each person entering production premises must be trained on the procedure of gowning and de-gowning. There are three types of gowning uses in manufacturing operations. These include Primary gowning, secondary gowning, and tertiary gowning. Operations personnel must wear freshly cleaned gowns daily. Pharmaceuticals owns an in-house laundry system to ensure clean and contamination-free gowning.
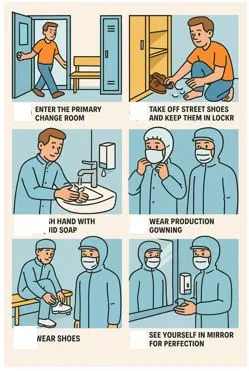
Personnel and Material Flow
Personal and material flow are important aspects of GMP. Improper personal flow may lead to contamination or any blunder in manufacturing operations. To prevent contamination, there are two types of airlocks. One is PAL (Personal air lock) and the other is MAL (Material air lock).
Personal flow is dedicated to the movement of personnel working in the pharmaceutical operations. Personnel are restricted from entering the premises without proper dedicated gowning. Personnel are not allowed to move freely in other sections.
There are multiple stages of personnel gowning:
- The first stage is the Primary change room, where Primary gowning is worn by the personnel to enter the non-classified area of production.
- The second stage is the secondary change room, where personnel wear secondary gowning in a class D environment to enter in class D corridor.
- The third stage is the tertiary change room, where the personnel wear tertiary gowning and enter the manufacturing cubicle.
Material movements are not allowed from the personnel moving areas. Different types of materials move from one section to another.
Below are some examples of material movement.
- Raw Material moves from the raw material staging racks to the dispensary for dispensing, utilizing the material air lock of the dispensary for movement.
- Movement of the dispensed batch from the staging section of Production to the respective granulation suite via the material air lock of granulation.
- Movement of granules from WIP (Work In-Process Section) to respective Compression cubicles via the material air lock of compression.
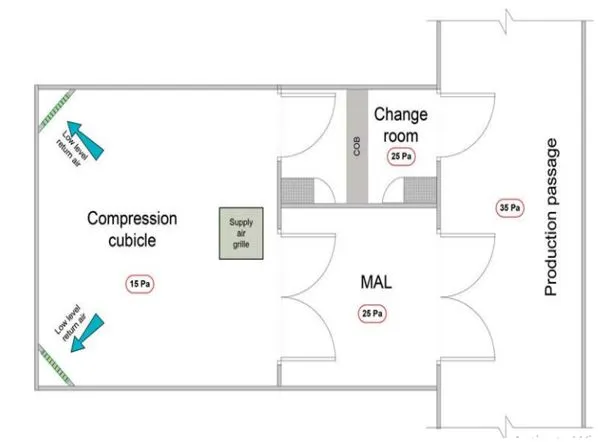
Premises
Pharmaceutical premises are a crucial aspect of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP).
- The structure of the premises should have good height and sufficient lighting intensity.
- Proper epoxy paint and flooring should be done in such a way that promotes smooth cleaning. Walls, floor, and Roof of the premises should be free from cracks and any damage.
- A proper maintenance plan should be in place for facility maintenance.
- Change rooms, amenities, lockers, supply ducts, return ducts, and drains of the section should be designed in such a way that ensures proper cleaning.
- The drainage system has vast importance, and it must prevent backflow.
- Sanitization of drainage with a disinfectant is mandatory every week.
- There should be a perfect installation of utilities.
- Inert chemicals should be used for the fabrication of walls and the roof.
Machines
The utilization of machinery and instruments in pharmaceutical operations must be GMP compliant.
- Machines should be installed properly. It must avoid space limitations, ensuring adequate clearance on all four sides for the unobstructed movement of personnel and machine parts.
- The material of construction used for the fabrication of machines must be inert and must not possess a chemical or physical reaction upon direct contact with the drug.
“SS316L is the most suitable material for pharmaceutical production areas, as it offers superior durability and resists leaching, ensuring product safety and equipment longevity.”
- Machines should be designed in such a way that each part of the machine is easily cleanable.
- Eliminate hidden spaces of the machine that promote microbial growth or any possibility of cross-contamination.
- Good machines ensure smooth cleaning and worker safety.
- Machines should be automated and a closed system.
- A closed system is recommended to prevent product exposure within the environment and to ensure personal safety.
- A good recording system is recommended for GMP-compliant machines.
- A good machine ensures administrative control and limits manual controls.
Consider an example of a High Shear Mixer,
A High Shear Mixer should be capable of mixing powders, granules, and it is equipped with a chopper and a mixer located inside. An upper lid for material input and an outlet with a sieve for ejection of mixed material. High shear.
- Installed properly with sufficient spaces on all sides of the machines to ensure free movement and cleaning provision for the surroundings of the machine.
- Fabrication of material is SS316L
- Visibility of parameters, including RPM and time of the chopper and mixer.
- Recording of data is centralized or should be within the machine.
- The password control system is provided with three levels of security. The first level is the Administrative level. This level has all controls. The second level is the Engineering controls. The third level is the Operator control.
- Parameters are locked and unchangeable as per the validated recipe.
Quality Control
Quality control is an integral part of any pharmaceutical organization. QC ensures product safety, identity, strength, purity, and quality of the drug product. The QC department is equipped with qualified personnel and appropriate instruments. Equipment commonly used in QC includes HPLC, UV spectrophotometer, pH Meter, and conductivity meter. and others. The QC department is responsible for testing products according to the criteria defined in the SOP.
QC has approved testing methods. Many standards define testing criteria for raw materials and finished products. Commonly used standards include the United States Pharmacopeia, the British Pharmacopeia, and the Japanese Pharmacopeia. Sometimes, the method is not yet proposed by any standard, so QC defines an in-house validated method.
QC tests representative samples of each batch of a product and tests according to standards. QC ensures GLP, i.e., Good Laboratory Practices. QC equipment must be CFR21 qualified. Each user has a separate ID provided to ensure data integrity and prevent breach of data breaches. A good QC system keeps the audit trails and ensures the backup of data. QC is the backbone of any pharma industry. QC is the final assurance of the quality of the drug product.
Batch Documents
Documentation of each step should be kept recorded either electronically or on paper. These documents are suggested to be kept for over one year after the completion of the shelf life of a product. This practice is helpful in any market complaint or any adverse reaction traceability.
Batch documents are given high consideration in GMP because they contain the data from the start of the manufacturing till the end of the product and final testing report by QC as well.
Batch documents contain the data of every step, and they provide information regarding who performed it, when it was performed, where performed it and what was performed. Batch documents must abide by the GDP rules. GDP is a good documentation practice and an integral part of GMP. Personnel working in pharmaceutical operations must be trained on GDP. There are some examples of GDP violations.


Validation
Validation is documented evidence that provides certainty that the process that was performed gives reproducible results. Validation is a mandatory part of GMP and is recommended to validate equipment, process, and product. In pharmaceuticals, whether it is the HVAC system or water system, it is a mandatory regulatory requirement to perform its validation. In validation studies, qualified persons prepare the protocol and perform necessary documentation. When the validation has been done, authorized persons prepare the validation report.
After successful validation, VSR is also generated, called validation summary reports, containing the summary of total activities and recommendations.
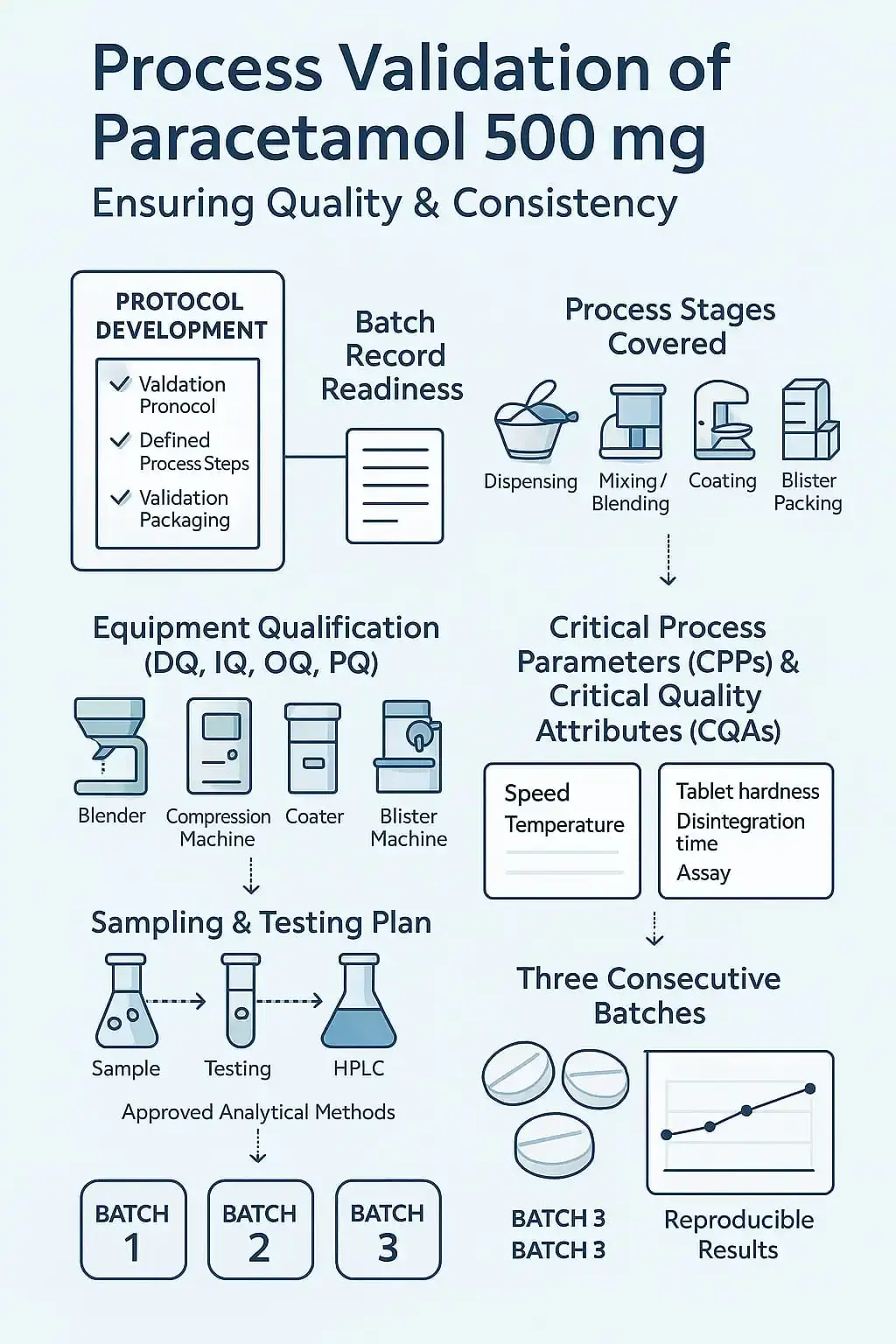
The following steps will be followed,
- Writing protocol and defining steps
- The batch record is ready
- All steps covered in the validation protocol, i.e,. dispensing till packaging of paracetamol 500 mg
- All equipment involved in the operation is qualified, like DQ (Design qualification) IQ (Installation qualification). OQ (Operational qualification), PQ (Performance qualification) have been performed for the equipment. E.g. Blender, compression machine, coating, blister machine are qualified.
- Establish CPPs and CQAs of paracetamol 500 mg.
- Plan sampling criteria at each stage and testing criteria as per the approved method.
- Plan three batches consecutively to ensure reproducible results
- The approved testing method is available
- The testing method gives reproducible results for the manufactured batch of paracetamol 500 mg.
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System(HVAC)
HVAC system is also called as heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system. Pharmaceutical organizations are incomplete without installing HVAC system. HVAC system ensures to provide the controlled temperature, humidity, and cleanliness level required. HVAC systems should be designed in such a way that it must have the desired capacity to control cooling, heating, humidification, and dehumidification of areas and air volumes. The HVAC system maintains the clean room classification. There are usages of pre-filters, HEPA Filters, and ULPA filters, which can provide an efficiency of cleaned air of 99.99%.
Water System
The water system is also an important aspect in GMP. Water is required for different purposes in pharmaceutical operations. Water is required for general facilities, washing of equipment and utensils, batch manufacturing, preparations of solvents, and is required in general utilities and QC. This usage of water determines its importance in the manufacturing industry.
It is mandatory to perform the necessary chemical testing and check the microbiological load of water before production use. This water is usually called water for pharmaceutical use (WPU). It is mandatory to have strict control parameters for water testing. The following management is required for WPU. I.e., a proper water treatment system, a proper water storage and distribution system, proper commissioning of the water distribution system, and their qualification and validation. Sampling and testing points, routine monitoring, and release of water by QC. There should be an SOP on the sanitization of loops and utilities used for the storage and transfer of water within the plant premises.
Pharmacopeia, i.e., USP and BP, defines the quality of water to be tested before use in production. There are some types that are mentioned in the WHO guidelines and are briefly described below.
1. Drinking Water
Drinking water is required in pharmaceuticals for human consumption. Drinking water is produced from raw water by some special treatments like filtration, softening to make it soft for human consumption. To make drinking water, desalination, softening, filtration, disinfection, iron removal, and reduction in concentration of specific organic and inorganic materials are employed.
2. Bulk Purified Water
This water is prepared from the drinking water. Several methods to prepare BPW, i.e., Reverse Osmosis, electrodeionization (EDI). Sometimes, a combination of methods is used to prepare BPW. Thermal and chemical sanitization is required at periodic intervals defined in the SOP derived from the qualification validating reports. Usually, this water is kept in circulation at a standard temperature of around 70 to 80 oC pre-validated.
3. Bulk Water For Injection
This water should meet the pharmacopeia specifications. BWFI is the highest quality of water used in pharmaceuticals. This water should be free from microbiological contaminants, including endotoxins. Its application is in sterile product manufacturing and final rinsing of primary containers. Usually, this water is kept in circulation at a standard temperature of around 70 to 80 oC pre-validated.
The importance of the water system cannot be ignored in pharmaceutical companies for the manufacturing of medicines.
The following table will illustrate the usage and preparation, and specifications of water.
| 1. Drinking Water | 2. Bulk Purified Water | Bulk Water For Injection |
Water that is supplied by the municipal corporation from the rivers | Drinking water, when treated with some special treatments, is converted to purified water | Highly purified water which is free from endotoxins and microbes |
| Highly purified water, which is free from endotoxins and microbes | Uses: This water is being used in pharmaceuticals for non-sterile products manufacturing and washing of equipment. | Uses: This water is being used in the manufacturing of sterile products and washing of sterile primary containers before the step of Depyrogenation |
| Method of Manufacture: This water is treated with chlorination and filtration. | Method of Manufacture: Distillation, Reverse Osmosis. | Method of Manufacture: Distillation, Ultrafiltration |
| Microbial Load: <500 CFU/ml | Microbial Load: Total viable aerobic count: ≤ 100 CFU/ml. Combined Molds and Yeast count: ≤ 10 CFU/ml Absence of Pathogens | Microbial Load: Total viable aerobic count: ≤ 10 CFU/100 ml. Bacterial Endotoxins: ≤0.25EU/ml |
| Conductance at 25OC: Around 500 to 800 (µS/cm). Its limit may vary depending upon the source. | Conductance at 25 °C: ≤1.3 (µS/cm) | Conductance at 25OC: Around 500 to 800 (µS/cm). Its limit may vary depending on the source. |
| TOC: (Total Organic Carbon) Not specified | TOC: (Total Organic Carbon) ≤500ppb | TOC: (Total Organic Carbon) ≤500ppb |
Housekeeping System
Good housekeeping is required to maintain GMP in a pharmaceutical plant. Whether it is the QC lab or QA, or Toilet facilities, cleaning is mandatory. There should be a proper cleaning system in place and in use to ensure the cleaning of walls, floors, and drains. Qualified disinfectants should be used, like Dettol or quaternary ammonium compounds. Disinfectants should possess antimicrobial qualities, and different disinfectants should be used over time to prevent microbial resistance to disinfectants.
A good practice is to prepare a schedule for the use of disinfectants. Items used for housekeeping must be dedicated to each section to prevent contamination. Cleaning tools must be cleaned and washed daily before and after use. The cleaning tool must be fabricated with good materials like stainless steel or non-shredding material. If the housekeeping system of any pharmaceutical is not effective so serious noncompliance issues will be observed.
Active Ingredients and Excipients
In pharmaceuticals, APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) and Excipients are converted to form a drug product as per the approved formulation. Use of APIs and Excipients is an important consideration in GMP.
Before production use, APIs and Excipients must be tested for quality as per the method defined in the pharmacopeia. The established specifications of APIs and Excipients should not be changed upon a change of the lot of API or Excipients. Any change in the specification of the API or excipient will impact the critical quality attributes of a product. This change may impact on product assay, product dissolution, or variation in the physical characteristics of the product.
Storage Areas
Storage areas of pharmaceuticals must be cleaned, with space for proper palletization, temperature, and RH controlled as per the requirements of the area. There are different storage areas in pharmaceutical operations. The Raw Material store is deputed for the storage of raw materials used to manufacture the drug product. The packaging material store is deputed to store primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging materials. Quarantine areas are used to store the unreleased material. A WIP (Work in process) store is deputed for the temporary storage of products which has not yet been completed but are in the form of semi-finished products.
Conclusion
In any pharmaceutical operation, GMP is mandatory to be maintained throughout the product life cycle. This is an international regulatory requirement. International agencies like ISO, PIC/S perform audits to certify pharmaceutical organizations. To ensure the cGMP operations, companies carry out validation activities that ensure that the product will be consistently produced without any variation. GMP is not just confined to production operations but spreads throughout the plant premises till the consumption of its final unit, whether it is the change room, janitorial, HVAC system, QC, quality assurance, warehouses or transportation, or retail stores. All the stakeholders are responsible for working with GMP to ensure product integrity throughout its shelf life.
References
https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/medicines-good-manufacturing-processes
https://picscheme.org/docview/6606
https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/trs1019-annex2
TRS 1019 Annexure 3 Validation
TRS 1033: water for pharmaceutical use

